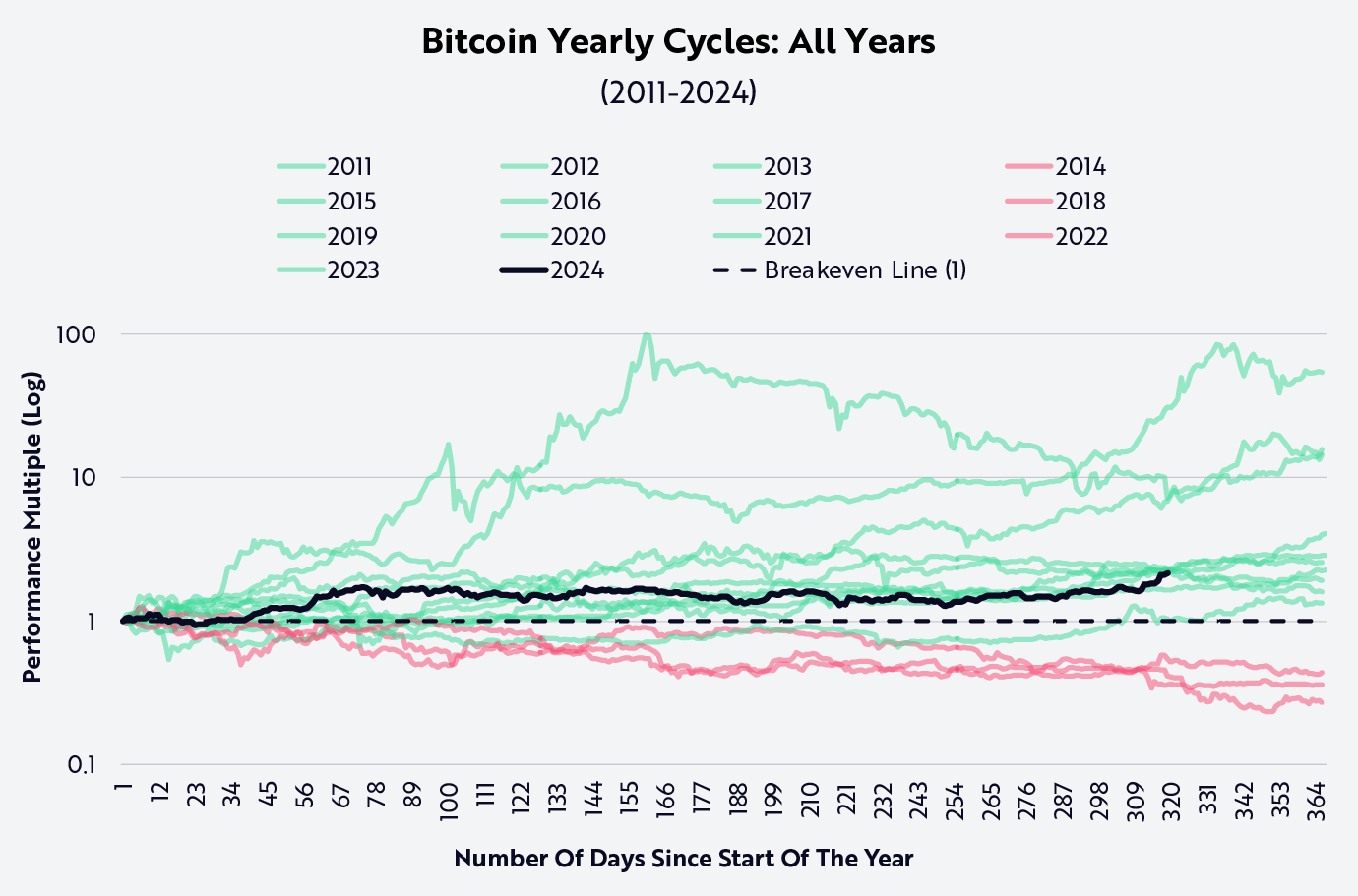
The world of cryptocurrency, particularly Bitcoin, is often described as unpredictable and volatile. Bitcoin cycles are integral to understanding the broader cryptocurrency market’s fluctuations, trends, and patterns. These cycles refer to the recurring phases of price rises and falls that occur in the Bitcoin market over time. In this blog post, I’ll explore Bitcoin cycles in-depth, shedding light on the key factors that drive these patterns, and offering insights into how investors can navigate these cycles effectively.
Understanding Bitcoin Cycles
Bitcoin cycles are crucial for both novice and experienced cryptocurrency investors. A Bitcoin cycle typically refers to the ups and downs in the price of Bitcoin, which usually follow a repetitive pattern over several months or years. Investors and traders closely monitor these cycles to time their purchases and sales for maximum profit.
1. The Bull Market: Bitcoin’s Upward Surge
A Bitcoin cycle generally starts with the bull market phase, a period where Bitcoin’s price experiences rapid upward growth. This phase is marked by strong market optimism, increased media coverage, and growing investor interest. As more people begin to buy Bitcoin, the price rises, leading to a widespread sense of euphoria in the market.
2. The Bear Market: A Period of Decline
After a bull market, Bitcoin often enters a bear market, characterized by a sharp decline in price. The mood shifts from optimism to fear as investors begin to sell off their assets to cut their losses. This is where the market experiences a major downturn, and prices can plummet by significant margins. Understanding the bear market is crucial for managing risk, as this phase represents the period of maximum uncertainty.
3. Consolidation: The Calm Before the Storm
Following a bear market, Bitcoin often enters a consolidation phase. During this period, the price stabilizes, and the market sentiment becomes neutral. Investors who have stayed through the previous phases might either wait for a clear trend or start accumulating Bitcoin at lower prices. This phase is essential for setting up the next bull market cycle.
4. Halving and its Impact on Bitcoin Cycles
One of the most unique factors influencing Bitcoin cycles is the halving event. Bitcoin halving occurs approximately every four years and reduces the reward miners receive for validating transactions on the network. The reduction in supply often leads to increased demand, which can trigger a new bull market cycle. Understanding how halving works can help investors predict potential upward trends in the Bitcoin price.
5. External Factors Affecting Bitcoin Cycles
While Bitcoin cycles are primarily driven by market dynamics, external factors can also play a significant role in influencing price movements. For instance, macroeconomic events such as global financial crises, government regulations, or technological advancements can alter the trajectory of Bitcoin’s cycles. Keeping an eye on these external factors is essential for any investor aiming to anticipate the next phase in the Bitcoin cycle.
6. The Role of Media and Public Perception
Public perception and media coverage can significantly affect the length and intensity of Bitcoin cycles. Positive news, such as institutional adoption or favorable regulations, can fuel the bull market, while negative news, such as hacks or bans in certain countries, can exacerbate the bear market. Investors should stay updated with the latest news to gauge market sentiment accurately.
7. Psychological Factors in Bitcoin Cycles
The psychology of investors plays a critical role in Bitcoin cycles. During a bull market, greed can push investors to buy at the peak of the cycle, only to sell in panic during a bear market. Conversely, fear of missing out (FOMO) can drive prices to unsustainable levels. Understanding these psychological factors can help investors avoid common mistakes and make more informed decisions.
8. Technical Analysis and Bitcoin Cycles
For those looking to capitalize on Bitcoin cycles, technical analysis is a vital tool. Using charts, indicators, and patterns, traders attempt to predict the direction of Bitcoin’s price movement. Technical analysis can provide valuable insights into potential entry and exit points during different phases of the cycle.
9. Fundamental Analysis and Bitcoin Cycles
Beyond technical analysis, fundamental analysis also plays a role in understanding Bitcoin cycles. Factors such as Bitcoin’s market capitalization, network activity, and adoption rates can offer insight into the long-term viability of the cryptocurrency and how it might behave in future cycles. Fundamental analysis helps investors look past short-term price fluctuations and assess Bitcoin’s underlying value.
10. Identifying Market Cycles Using Data
Bitcoin cycles are not purely driven by speculation or sentiment. They can also be identified using data-driven approaches. Tools such as the Bitcoin stock-to-flow model or on-chain analysis can help predict future price trends by examining Bitcoin’s supply and demand characteristics. Investors can use these data points to time their trades better.
11. Risk Management in Bitcoin Cycles
Given the inherent volatility of Bitcoin, risk management is crucial when navigating its cycles. By setting stop-loss orders and diversifying your portfolio, you can minimize potential losses during the inevitable downturns. Additionally, understanding the cyclical nature of Bitcoin can help you set realistic profit targets and avoid making hasty decisions based on short-term price movements.
12. Bitcoin Cycles in 2025: What to Expect
As Bitcoin approaches 2025, the cryptocurrency’s market is likely to undergo new cycles that will be shaped by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and broader economic factors. Although predicting the exact timing of these cycles is difficult, the ongoing adoption of Bitcoin by both institutional investors and retail users is likely to play a crucial role in determining future market phases.
13. The Importance of Patience in Bitcoin Cycles
Investing in Bitcoin requires patience. Cycles can last anywhere from months to years, and the market can sometimes seem unpredictable. However, understanding the broader patterns and maintaining a long-term perspective can help investors avoid rash decisions and take advantage of Bitcoin’s potential for growth over time.
14. Conclusion: Navigating the Cycles with Strategy
In conclusion, Bitcoin cycles are an essential aspect of cryptocurrency investing. By understanding the phases of Bitcoin’s market cycle – from the bull market to the bear market – and applying strategic tools such as technical and fundamental analysis, investors can better navigate this volatile market. Whether you’re new to Bitcoin or an experienced trader, recognizing the cyclical nature of Bitcoin is key to making smarter investment decisions.
For more information on Bitcoin halving events and their historical impact on market cycles, check out this comprehensive guide.